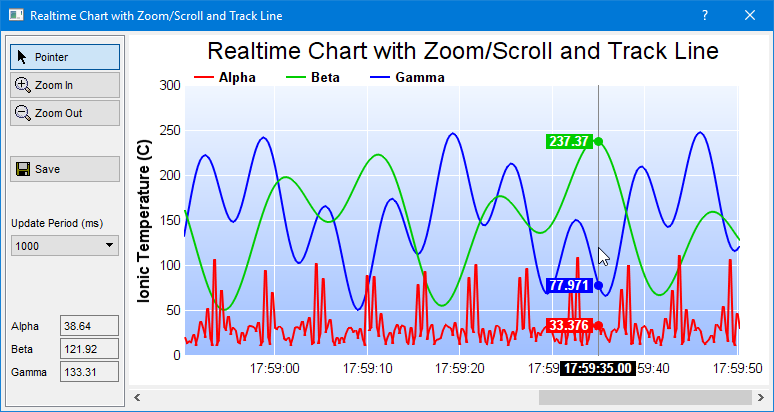
[Qt Widgets version] qtdemo/realtimezoomscroll.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include <QIcon>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QFileDialog>
#include "realtimezoomscroll.h"
#include "chartdir.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
static const int DataInterval = 250;
RealTimeZoomScroll::RealTimeZoomScroll(QWidget *parent) :
QDialog(parent)
{
//
// Set up the GUI
//
setFixedSize(772, 380);
setWindowTitle("Real-Time Chart with Zoom/Scroll and Track Line");
QFrame *frame = new QFrame(this);
frame->setGeometry(4, 4, 120, 372);
frame->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
// Pointer push button
QPushButton *pointerPB = new QPushButton(QIcon(":/icons/scroll_icon.png"), "Scroll", frame);
pointerPB->setGeometry(4, 8, 112, 28);
pointerPB->setStyleSheet("QPushButton { text-align:left; padding:5px}");
pointerPB->setCheckable(true);
// Zoom In push button
QPushButton *zoomInPB = new QPushButton(QIcon(":/icons/zoomin_icon.png"), "Zoom In", frame);
zoomInPB->setGeometry(4, 36, 112, 28);
zoomInPB->setStyleSheet("QPushButton { text-align:left; padding:5px}");
zoomInPB->setCheckable(true);
// Zoom Out push button
QPushButton *zoomOutPB = new QPushButton(QIcon(":/icons/zoomout_icon.png"), "Zoom Out", frame);
zoomOutPB->setGeometry(4, 64, 112, 28);
zoomOutPB->setStyleSheet("QPushButton { text-align:left; padding:5px}");
zoomOutPB->setCheckable(true);
// Save push button
QPushButton *savePB = new QPushButton(QIcon(":/icons/save_icon.png"), "Save", frame);
savePB->setStyleSheet("QPushButton { text-align:left; padding:5px}");
savePB->setGeometry(4, 120, 112, 28);
connect(savePB, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), SLOT(onSave(bool)));
// The Pointer/Zoom In/Zoom Out buttons form a button group
mouseUsage = new QButtonGroup(frame);
mouseUsage->addButton(pointerPB, Chart::MouseUsageScroll);
mouseUsage->addButton(zoomInPB, Chart::MouseUsageZoomIn);
mouseUsage->addButton(zoomOutPB, Chart::MouseUsageZoomOut);
connect(mouseUsage, SIGNAL(buttonPressed(QAbstractButton*)),
SLOT(onMouseUsageChanged(QAbstractButton*)));
// Update Period drop down list box
(new QLabel("Update Period (ms)", frame))->setGeometry(6, 180, 108, 16);
updatePeriod = new QComboBox(frame);
updatePeriod->setGeometry(6, 200, 108, 21);
updatePeriod->addItems(QStringList() << "250" << "500" << "750" << "1000" << "1250" << "1500"
<< "1750" << "2000");
connect(updatePeriod, SIGNAL(currentIndexChanged(int)), SLOT(onUpdatePeriodChanged(int)));
// Alpha Value display
(new QLabel("Alpha", frame))->setGeometry(6, 280, 48, 21);
m_ValueA = new QLabel(frame);
m_ValueA->setGeometry(55, 280, 59, 21);
m_ValueA->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
// Beta Value display
(new QLabel("Beta", frame))->setGeometry(6, 303, 48, 21);
m_ValueB = new QLabel(frame);
m_ValueB->setGeometry(55, 303, 59, 21);
m_ValueB->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
// Gamma Value display
(new QLabel("Gamma", frame))->setGeometry(6, 326, 48, 21);
m_ValueC = new QLabel(frame);
m_ValueC->setGeometry(55, 326, 59, 21);
m_ValueC->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
// Chart Viewer
m_ChartViewer = new QChartViewer(this);
m_ChartViewer->setGeometry(128, 4, 640, 350);
connect(m_ChartViewer, SIGNAL(viewPortChanged()), SLOT(onViewPortChanged()));
connect(m_ChartViewer, SIGNAL(mouseMovePlotArea(QMouseEvent*)),
SLOT(onMouseMovePlotArea(QMouseEvent*)));
// Horizontal scroll bar
m_HScrollBar = new QScrollBar(Qt::Horizontal, this);
m_HScrollBar->setGeometry(128, 358, 640, 17);
connect(m_HScrollBar, SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)), SLOT(onHScrollBarChanged(int)));
// Clear data arrays to Chart::NoValue
for (int i = 0; i < sampleSize; ++i)
m_timeStamps[i] = m_dataSeriesA[i] = m_dataSeriesB[i] = m_dataSeriesC[i] = Chart::NoValue;
m_currentIndex = 0;
// Set m_nextDataTime to the current time. It is used by the real time random number
// generator so it knows what timestamp should be used for the next data point.
m_nextDataTime = QDateTime::currentDateTime();
// Initially set the mouse to drag to scroll mode.
pointerPB->click();
// Enable mouse wheel zooming by setting the zoom ratio to 1.1 per wheel event
m_ChartViewer->setMouseWheelZoomRatio(1.1);
// Set up the data acquisition mechanism. In this demo, we just use a timer to get a
// sample every 250ms.
QTimer *dataRateTimer = new QTimer(this);
dataRateTimer->start(DataInterval);
connect(dataRateTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), SLOT(onDataTimer()));
// Set up the chart update timer
m_ChartUpdateTimer = new QTimer(this);
connect(m_ChartUpdateTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), SLOT(onChartUpdateTimer()));
// Can start now
m_ChartUpdateTimer->start();
}
RealTimeZoomScroll::~RealTimeZoomScroll()
{
delete m_ChartViewer->getChart();
}
//
// The Pointer, Zoom In or Zoom out button is pressed
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onMouseUsageChanged(QAbstractButton *b)
{
m_ChartViewer->setMouseUsage(mouseUsage->id(b));
}
//
// The Save button is pressed
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onSave(bool)
{
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, "Save", "chartdirector_demo",
"PNG (*.png);;JPG (*.jpg);;GIF (*.gif);;BMP (*.bmp);;SVG (*.svg);;PDF (*.pdf)");
if (!fileName.isEmpty())
{
// Save the chart
BaseChart *c = m_ChartViewer->getChart();
if (0 != c)
c->makeChart(fileName.toUtf8().constData());
}
}
//
// User changes the chart update period
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onUpdatePeriodChanged(int)
{
m_ChartUpdateTimer->start(updatePeriod->currentText().toInt());
}
//
// The data acquisition routine. In this demo, this is invoked every 250ms.
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onDataTimer()
{
// The current time
QDateTime now = QDateTime::currentDateTime();
// This is our formula for the random number generator
do
{
// We need the currentTime in millisecond resolution
qint64 t = m_nextDataTime.toMSecsSinceEpoch();
double currentTime = Chart::chartTime2((int)(t / 1000)) + (t % 1000) / 250 * 0.25;
// Get a data sample
double p = currentTime * 4;
double dataA = 20 + cos(p * 129241) * 10 + 1 / (cos(p) * cos(p) + 0.01);
double dataB = 150 + 100 * sin(p / 27.7) * sin(p / 10.1);
double dataC = 150 + 100 * cos(p / 6.7) * cos(p / 11.9);
// In this demo, if the data arrays are full, the oldest 5% of data are discarded.
if (m_currentIndex >= sampleSize)
{
m_currentIndex = sampleSize * 95 / 100 - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < m_currentIndex; ++i)
{
int srcIndex = i + sampleSize - m_currentIndex;
m_timeStamps[i] = m_timeStamps[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesA[i] = m_dataSeriesA[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesB[i] = m_dataSeriesB[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesC[i] = m_dataSeriesC[srcIndex];
}
}
// Store the new values in the current index position, and increment the index.
m_timeStamps[m_currentIndex] = currentTime;
m_dataSeriesA[m_currentIndex] = dataA;
m_dataSeriesB[m_currentIndex] = dataB;
m_dataSeriesC[m_currentIndex] = dataC;
++m_currentIndex;
m_nextDataTime = m_nextDataTime.addMSecs(DataInterval);
}
while (m_nextDataTime < now);
//
// We provide some visual feedback to the latest numbers generated, so you can see the
// data being generated.
//
m_ValueA->setText(QString::number(m_dataSeriesA[m_currentIndex - 1], 'f', 2));
m_ValueB->setText(QString::number(m_dataSeriesB[m_currentIndex - 1], 'f', 2));
m_ValueC->setText(QString::number(m_dataSeriesC[m_currentIndex - 1], 'f', 2));
}
//
// Update the chart and the viewport periodically
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onChartUpdateTimer()
{
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
{
//
// As we added more data, we may need to update the full range of the viewport.
//
double startDate = m_timeStamps[0];
double endDate = m_timeStamps[m_currentIndex - 1];
// Use the initialFullRange (which is 60 seconds in this demo) if this is sufficient.
double duration = endDate - startDate;
if (duration < initialFullRange)
endDate = startDate + initialFullRange;
// Update the full range to reflect the actual duration of the data. In this case,
// if the view port is viewing the latest data, we will scroll the view port as new
// data are added. If the view port is viewing historical data, we would keep the
// axis scale unchanged to keep the chart stable.
int updateType = Chart::ScrollWithMax;
if (m_ChartViewer->getViewPortLeft() + m_ChartViewer->getViewPortWidth() < 0.999)
updateType = Chart::KeepVisibleRange;
bool scaleHasChanged = m_ChartViewer->updateFullRangeH("x", startDate, endDate, updateType);
// Set the zoom in limit as a ratio to the full range
m_ChartViewer->setZoomInWidthLimit(zoomInLimit / (m_ChartViewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", 1) -
m_ChartViewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", 0)));
// Trigger the viewPortChanged event to update the display if the axis scale has changed
// or if new data are added to the existing axis scale.
if (scaleHasChanged || (duration < initialFullRange))
m_ChartViewer->updateViewPort(true, false);
}
}
//
// View port changed event
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onViewPortChanged()
{
// In addition to updating the chart, we may also need to update other controls that
// changes based on the view port.
updateControls(m_ChartViewer);
// Update the chart if necessary
if (m_ChartViewer->needUpdateChart())
drawChart(m_ChartViewer);
}
//
// User clicks on the the horizontal scroll bar
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onHScrollBarChanged(int value)
{
if (!m_ChartViewer->isInViewPortChangedEvent())
{
// Set the view port based on the scroll bar
int scrollBarLen = m_HScrollBar->maximum() + m_HScrollBar->pageStep();
m_ChartViewer->setViewPortLeft(value / (double)scrollBarLen);
// Update the chart display without updating the image maps. (We can delay updating
// the image map until scrolling is completed and the chart display is stable.)
m_ChartViewer->updateViewPort(true, false);
}
}
//
// Update controls in the user interface when the view port changed
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::updateControls(QChartViewer *viewer)
{
// The logical length of the scrollbar. It can be any large value. The actual value does
// not matter.
const int scrollBarLen = 1000000000;
// Update the horizontal scroll bar
m_HScrollBar->setEnabled(viewer->getViewPortWidth() < 1);
m_HScrollBar->setPageStep((int)ceil(viewer->getViewPortWidth() * scrollBarLen));
m_HScrollBar->setSingleStep((std::min)(scrollBarLen / 100, m_HScrollBar->pageStep()));
m_HScrollBar->setRange(0, scrollBarLen - m_HScrollBar->pageStep());
m_HScrollBar->setValue((int)(0.5 + viewer->getViewPortLeft() * scrollBarLen));
}
//
// Draw chart
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::drawChart(QChartViewer *viewer)
{
// Get the start date and end date that are visible on the chart.
double viewPortStartDate = viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", viewer->getViewPortLeft());
double viewPortEndDate = viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", viewer->getViewPortLeft() +
viewer->getViewPortWidth());
// Extract the part of the data arrays that are visible.
DoubleArray viewPortTimeStamps;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesA;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesB;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesC;
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
{
// Get the array indexes that corresponds to the visible start and end dates
int startIndex = (int)floor(Chart::bSearch(DoubleArray(m_timeStamps, m_currentIndex), viewPortStartDate));
int endIndex = (int)ceil(Chart::bSearch(DoubleArray(m_timeStamps, m_currentIndex), viewPortEndDate));
int noOfPoints = endIndex - startIndex + 1;
// Extract the visible data
viewPortTimeStamps = DoubleArray(m_timeStamps+ startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesA = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesA + startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesB = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesB + startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesC = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesC + startIndex, noOfPoints);
}
//
// At this stage, we have extracted the visible data. We can use those data to plot the chart.
//
//================================================================================
// Configure overall chart appearance.
//================================================================================
// Create an XYChart object of size 640 x 350 pixels
XYChart *c = new XYChart(640, 350);
// Set the plotarea at (55, 50) with width 80 pixels less than chart width, and height 80 pixels
// less than chart height. Use a vertical gradient from light blue (f0f6ff) to sky blue (a0c0ff)
// as background. Set border to transparent and grid lines to white (ffffff).
c->setPlotArea(55, 50, c->getWidth() - 85, c->getHeight() - 80, c->linearGradientColor(0, 50, 0,
c->getHeight() - 35, 0xf0f6ff, 0xa0c0ff), -1, Chart::Transparent, 0xffffff, 0xffffff);
// As the data can lie outside the plotarea in a zoomed chart, we need enable clipping.
c->setClipping();
// Add a title to the chart using 18pt Arial font
c->addTitle(" Realtime Chart with Zoom/Scroll and Track Line", "Arial", 18);
// Add a legend box at (55, 25) using horizontal layout. Use 10pt Arial Bold as font. Set the
// background and border color to transparent and use line style legend key.
LegendBox *b = c->addLegend(55, 25, false, "Arial Bold", 10);
b->setBackground(Chart::Transparent);
b->setLineStyleKey();
// Set the x and y axis stems to transparent and the label font to 10pt Arial
c->xAxis()->setColors(Chart::Transparent);
c->yAxis()->setColors(Chart::Transparent);
c->xAxis()->setLabelStyle("Arial", 10);
c->yAxis()->setLabelStyle("Arial", 10);
// Set the y-axis tick length to 0 to disable the tick and put the labels closer to the axis.
c->yAxis()->setTickLength(0);
// Add axis title using 12pt Arial Bold Italic font
c->yAxis()->setTitle("Ionic Temperature (C)", "Arial Bold", 12);
//================================================================================
// Add data to chart
//================================================================================
//
// In this example, we represent the data by lines. You may modify the code below to use other
// representations (areas, scatter plot, etc).
//
// Add a line layer for the lines, using a line width of 2 pixels
LineLayer *layer = c->addLineLayer();
layer->setLineWidth(2);
layer->setFastLineMode();
// Now we add the 3 data series to a line layer, using the color red (ff0000), green (00cc00)
// and blue (0000ff)
layer->setXData(viewPortTimeStamps);
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesA, 0xff0000, "Alpha");
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesB, 0x00cc00, "Beta");
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesC, 0x0000ff, "Gamma");
//================================================================================
// Configure axis scale and labelling
//================================================================================
// Set the x-axis as a date/time axis with the scale according to the view port x range.
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
c->xAxis()->setDateScale(viewPortStartDate, viewPortEndDate);
// For the automatic axis labels, set the minimum spacing to 75/30 pixels for the x/y axis.
c->xAxis()->setTickDensity(75);
c->yAxis()->setTickDensity(30);
//
// In this demo, the time range can be from many hours to a few seconds. We can need to define
// the date/time format the various cases.
//
// If all ticks are hour algined, we use "hh:nn<*br*>mmm dd" in bold font as the first label of
// the Day, and "hh:nn" for other labels.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("align", 3600);
c->xAxis()->setMultiFormat(Chart::StartOfDayFilter(), "<*font=bold*>{value|hh:nn<*br*>mmm dd}",
Chart::AllPassFilter(), "{value|hh:nn}");
// If all ticks are minute algined, then we use "hh:nn" as the label format.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("align", 60);
c->xAxis()->setLabelFormat("{value|hh:nn}");
// If all other cases, we use "hh:nn:ss" as the label format.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("else");
c->xAxis()->setLabelFormat("{value|hh:nn:ss}");
// We make sure the tick increment must be at least 1 second.
c->xAxis()->setMinTickInc(1);
//================================================================================
// Output the chart
//================================================================================
// We need to update the track line too. If the mouse is moving on the chart (eg. if
// the user drags the mouse on the chart to scroll it), the track line will be updated
// in the MouseMovePlotArea event. Otherwise, we need to update the track line here.
if (!viewer->isInMouseMoveEvent())
{
trackLineLabel(c, (0 == viewer->getChart()) ? c->getPlotArea()->getRightX() :
viewer->getPlotAreaMouseX());
}
// Set the chart image to the QChartViewer
delete viewer->getChart();
viewer->setChart(c);
}
//
// Draw track cursor when mouse is moving over plotarea
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::onMouseMovePlotArea(QMouseEvent *)
{
trackLineLabel((XYChart *)m_ChartViewer->getChart(), m_ChartViewer->getPlotAreaMouseX());
m_ChartViewer->updateDisplay();
}
//
// Draw the track line with data point labels
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::trackLineLabel(XYChart *c, int mouseX)
{
// Clear the current dynamic layer and get the DrawArea object to draw on it.
DrawArea *d = c->initDynamicLayer();
// The plot area object
PlotArea *plotArea = c->getPlotArea();
// Get the data x-value that is nearest to the mouse, and find its pixel coordinate.
double xValue = c->getNearestXValue(mouseX);
int xCoor = c->getXCoor(xValue);
if (xCoor < plotArea->getLeftX())
return;
// Draw a vertical track line at the x-position
d->vline(plotArea->getTopY(), plotArea->getBottomY(), xCoor, 0x888888);
// Draw a label on the x-axis to show the track line position.
std::ostringstream xlabel;
xlabel << "<*font,bgColor=000000*> " << c->xAxis()->getFormattedLabel(xValue, "hh:nn:ss.ff")
<< " <*/font*>";
TTFText *t = d->text(xlabel.str().c_str(), "Arial Bold", 10);
// Restrict the x-pixel position of the label to make sure it stays inside the chart image.
int xLabelPos = (std::max)(0, (std::min)(xCoor - t->getWidth() / 2, c->getWidth() - t->getWidth()));
t->draw(xLabelPos, plotArea->getBottomY() + 6, 0xffffff);
t->destroy();
// Iterate through all layers to draw the data labels
for (int i = 0; i < c->getLayerCount(); ++i) {
Layer *layer = c->getLayerByZ(i);
// The data array index of the x-value
int xIndex = layer->getXIndexOf(xValue);
// Iterate through all the data sets in the layer
for (int j = 0; j < layer->getDataSetCount(); ++j)
{
DataSet *dataSet = layer->getDataSetByZ(j);
const char *dataSetName = dataSet->getDataName();
// Get the color, name and position of the data label
int color = dataSet->getDataColor();
int yCoor = c->getYCoor(dataSet->getPosition(xIndex), dataSet->getUseYAxis());
// Draw a track dot with a label next to it for visible data points in the plot area
if ((yCoor >= plotArea->getTopY()) && (yCoor <= plotArea->getBottomY()) && (color !=
Chart::Transparent) && dataSetName && *dataSetName)
{
d->circle(xCoor, yCoor, 4, 4, color, color);
std::ostringstream label;
label << "<*font,bgColor=" << std::hex << color << "*> "
<< c->formatValue(dataSet->getValue(xIndex), "{value|P4}") << " <*font*>";
t = d->text(label.str().c_str(), "Arial Bold", 10);
// Draw the label on the right side of the dot if the mouse is on the left side the
// chart, and vice versa. This ensures the label will not go outside the chart image.
if (xCoor <= (plotArea->getLeftX() + plotArea->getRightX()) / 2)
t->draw(xCoor + 6, yCoor, 0xffffff, Chart::Left);
else
t->draw(xCoor - 6, yCoor, 0xffffff, Chart::Right);
t->destroy();
}
}
}
}
[QML/Qt Quick version] qmldemo/realtimezoomscroll.qml
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Window
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtQuick.Dialogs
import advsofteng.com 1.0
Window {
title: "Real-Time Chart with Zoom/Scroll and Track Line"
visible: true
modality: Qt.ApplicationModal
width: 770
minimumWidth: 770
maximumWidth: 770
height: 380
minimumHeight: 380
maximumHeight: 380
Pane {
id: leftPane
width: 120
padding: 5
anchors.top: parent.top;
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom;
Column {
Button {
width: 110
contentItem: Row {
padding: 2; leftPadding: 5
Image { source: "icons/scroll_icon.png"; width:16; height:16; }
Text { text: " Pointer"; font.pixelSize: 13; }
}
checked: viewer.mouseUsage == QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageScroll
onClicked: viewer.mouseUsage = QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageScroll
}
Button
{
width: 110
contentItem: Row {
padding: 2; leftPadding: 5;
Image { source: "icons/zoomin_icon.png"; width:16; height:16; }
Text { text: " Zoom In"; font.pixelSize: 13; }
}
checked: viewer.mouseUsage == QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageZoomIn
onClicked: viewer.mouseUsage = QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageZoomIn
}
Button {
width: 110
contentItem: Row {
padding: 2; leftPadding: 5
Image { source: "icons/zoomout_icon.png"; width:16; height:16; }
Text { text: " Zoom Out"; font.pixelSize: 13; }
}
checked: viewer.mouseUsage == QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageZoomOut
onClicked: viewer.mouseUsage = QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageZoomOut
}
// Spacer
Item {width: 1; height: 30}
Button {
width: 110
contentItem: Row {
padding: 2; leftPadding: 5
Image { source: "icons/save_icon.png"; width:16; height:16; }
Text { text: " Save"; font.pixelSize: 12; }
}
onClicked: saveImageDialog.open()
FileDialog {
id: saveImageDialog
title: "Save"
currentFile: "chartdirector_demo"
fileMode: FileDialog.SaveFile
nameFilters: ["PNG (*.png);", "JPG (*.jpg)", "GIF (*.gif)", "BMP (*.bmp)", "SVG (*.svg)", "PDF (*.pdf)"]
onAccepted: demo.saveChartImage(viewer, selectedFile)
}
}
// Spacer
Item {width: 1; height: 30}
Text {
text: "Update Period (ms)"
bottomPadding: 3
}
ComboBox {
width: 110
model: ["100ms", "200ms", "300ms", "500ms", "700ms", "1000ms"]
onActivated: chartUpdateTimer.interval = parseInt(currentText)
}
}
Column {
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom;
anchors.bottomMargin: 20
spacing: 4
Row {
Text { text: "Alpha:"; width: 55 }
Rectangle {
width: 55
height: childrenRect.height + 4
border.color: "#888888"
Text { x: 3; id: alphaValue; }
}
}
Row {
Text { text: "Beta:"; width: 55 }
Rectangle {
width: 55
height: childrenRect.height + 4
border.color: "#888888"
Text { x: 3; id: betaValue; }
}
}
Row {
Text { text: "Gamma:"; width: 55 }
Rectangle {
width: 55
height: childrenRect.height + 4
border.color: "#888888"
Text { x: 3; id: gammaValue; }
}
}
}
}
QmlChartViewer
{
id: viewer
anchors.left: leftPane.right
anchors.leftMargin: 5
y: 5
// set default mouse usage to scroll and mouse wheel to zoom
mouseUsage: QmlChartViewer.MouseUsageScroll
mouseWheelZoomRatio: 1.1
// Update track cursor on mouse move
onMouseMovePlotArea: demo.drawTrackCursor(this, plotAreaMouseX)
// Update chart on viewport change. Update the scrollbar too.
onViewPortChanged: {
// redraw the chart
if (needUpdateChart)
demo.drawChart(this);
// update the scrollbar
hScrollBar.size = Math.min(viewer.viewPortWidth, 0.999999999);
hScrollBar.position = viewer.viewPortLeft;
}
}
// Add scrollbar under the chart viewer
ScrollBar
{
id: hScrollBar
orientation: Qt.Horizontal
height: 20
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
anchors.left: viewer.left
anchors.right: viewer.right
onPositionChanged: {
// The scrollbar and viewport can update each others. To avoid
// infinite loop, the scrollbar will update the viewport only
// if the viewport is not updating the scrollbar.
if (!viewer.isInViewPortChangedEvent) {
// update the viewport
viewer.viewPortLeft = this.position;
viewer.updateViewPort(true, false);
}
}
}
// The backend implementation of this demo.
RealTimeZoomScroll {
id: demo;
}
// This example uses a random number generator that generates a random
// number every 100ms. In real applications, the data can be generated
// by other means.
Timer {
interval:100; running: true; repeat: true
onTriggered: {
demo.getData();
alphaValue.text = demo.ValueA.toFixed(2);
betaValue.text = demo.ValueB.toFixed(2);
gammaValue.text = demo.ValueC.toFixed(2);
}
}
// The chart update timer. The chart can update at a different rate from
// the data, that is, asychronous update.
Timer {
id: chartUpdateTimer
interval:100; running: true ; repeat: true
onTriggered: demo.updateChart(viewer);
}
}
[QML/Qt Quick version] qmldemo/realtimezoomscroll.cpp
#include "realtimezoomscroll.h"
#include <sstream>
#include <math.h>
static const int DataInterval = 100;
RealTimeZoomScroll::RealTimeZoomScroll(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
m_currentChart = 0;
// Clear data arrays to Chart::NoValue
for (int i = 0; i < sampleSize; ++i)
m_timeStamps[i] = m_dataSeriesA[i] = m_dataSeriesB[i] = m_dataSeriesC[i] = Chart::NoValue;
m_currentIndex = 0;
// Set m_nextDataTime to the current time. It is used by the real time random number
// generator so it knows what timestamp should be used for the next data point.
m_nextDataTime = QDateTime::currentDateTime();
}
RealTimeZoomScroll::~RealTimeZoomScroll()
{
delete m_currentChart;
}
//
// The data acquisition routine. In this demo, this is invoked every DataInterval.
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::getData()
{
// The current time
QDateTime now = QDateTime::currentDateTime();
// This is our formula for the random number generator
do
{
// We need the currentTime in millisecond resolution
qint64 t = m_nextDataTime.toMSecsSinceEpoch();
double currentTime = Chart::chartTime2((int)(t / 1000)) + (t % 1000) / DataInterval
* DataInterval / 1000.0;
// Get a data sample
double p = currentTime * 4;
double dataA = 20 + cos(p * 129241) * 10 + 1 / (cos(p) * cos(p) + 0.01);
double dataB = 150 + 100 * sin(p / 27.7) * sin(p / 10.1);
double dataC = 150 + 100 * cos(p / 6.7) * cos(p / 11.9);
// In this demo, if the data arrays are full, the oldest 5% of data are discarded.
if (m_currentIndex >= sampleSize)
{
m_currentIndex = sampleSize * 95 / 100 - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < m_currentIndex; ++i)
{
int srcIndex = i + sampleSize - m_currentIndex;
m_timeStamps[i] = m_timeStamps[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesA[i] = m_dataSeriesA[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesB[i] = m_dataSeriesB[srcIndex];
m_dataSeriesC[i] = m_dataSeriesC[srcIndex];
}
}
// Store the new values in the current index position, and increment the index.
m_timeStamps[m_currentIndex] = currentTime;
m_dataSeriesA[m_currentIndex] = dataA;
m_dataSeriesB[m_currentIndex] = dataB;
m_dataSeriesC[m_currentIndex] = dataC;
++m_currentIndex;
m_nextDataTime = m_nextDataTime.addMSecs(DataInterval);
}
while (m_nextDataTime < now);
//
// We provide some visual feedback to the latest numbers generated, so you can see the
// data being generated.
//
m_ValueA = m_dataSeriesA[m_currentIndex - 1];
m_ValueB = m_dataSeriesB[m_currentIndex - 1];
m_ValueC = m_dataSeriesC[m_currentIndex - 1];
}
//
// Update the chart and the viewport periodically
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::updateChart(QmlChartViewer *viewer)
{
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
{
//
// As we added more data, we may need to update the full range of the viewport.
//
double startDate = m_timeStamps[0];
double endDate = m_timeStamps[m_currentIndex - 1];
// Use the initialFullRange (which is 60 seconds in this demo) if this is sufficient.
double duration = endDate - startDate;
if (duration < initialFullRange)
endDate = startDate + initialFullRange;
// Update the full range to reflect the actual duration of the data. In this case,
// if the view port is viewing the latest data, we will scroll the view port as new
// data are added. If the view port is viewing historical data, we would keep the
// axis scale unchanged to keep the chart stable.
int updateType = Chart::ScrollWithMax;
if (viewer->getViewPortLeft() + viewer->getViewPortWidth() < 0.999)
updateType = Chart::KeepVisibleRange;
bool scaleHasChanged = viewer->updateFullRangeH("x", startDate, endDate, updateType);
// Set the zoom in limit as a ratio to the full range
viewer->setZoomInWidthLimit(zoomInLimit / (viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", 1) -
viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", 0)));
// Trigger the viewPortChanged event to update the display if the axis scale has changed
// or if new data are added to the existing axis scale.
if (scaleHasChanged || (duration < initialFullRange))
viewer->updateViewPort(true, false);
}
}
//
// Draw chart
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::drawChart(QmlChartViewer *viewer)
{
// Get the start date and end date that are visible on the chart.
double viewPortStartDate = viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", viewer->getViewPortLeft());
double viewPortEndDate = viewer->getValueAtViewPort("x", viewer->getViewPortLeft() +
viewer->getViewPortWidth());
// Extract the part of the data arrays that are visible.
DoubleArray viewPortTimeStamps;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesA;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesB;
DoubleArray viewPortDataSeriesC;
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
{
// Get the array indexes that corresponds to the visible start and end dates
int startIndex = (int)floor(Chart::bSearch(DoubleArray(m_timeStamps, m_currentIndex), viewPortStartDate));
int endIndex = (int)ceil(Chart::bSearch(DoubleArray(m_timeStamps, m_currentIndex), viewPortEndDate));
int noOfPoints = endIndex - startIndex + 1;
// Extract the visible data
viewPortTimeStamps = DoubleArray(m_timeStamps+ startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesA = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesA + startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesB = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesB + startIndex, noOfPoints);
viewPortDataSeriesC = DoubleArray(m_dataSeriesC + startIndex, noOfPoints);
}
//
// At this stage, we have extracted the visible data. We can use those data to plot the chart.
//
//================================================================================
// Configure overall chart appearance.
//================================================================================
// Create an XYChart object of size 640 x 350 pixels
XYChart *c = new XYChart(640, 350);
// Set the plotarea at (55, 50) with width 80 pixels less than chart width, and height 80 pixels
// less than chart height. Use a vertical gradient from light blue (f0f6ff) to sky blue (a0c0ff)
// as background. Set border to transparent and grid lines to white (ffffff).
c->setPlotArea(55, 50, c->getWidth() - 85, c->getHeight() - 80, c->linearGradientColor(0, 50, 0,
c->getHeight() - 35, 0xf0f6ff, 0xa0c0ff), -1, Chart::Transparent, 0xffffff, 0xffffff);
// As the data can lie outside the plotarea in a zoomed chart, we need enable clipping.
c->setClipping();
// Add a title to the chart using 18pt Arial font
c->addTitle(" Realtime Chart with Zoom/Scroll and Track Line", "Arial", 18);
// Add a legend box at (55, 25) using horizontal layout. Use 10pt Arial Bold as font. Set the
// background and border color to transparent and use line style legend key.
LegendBox *b = c->addLegend(55, 25, false, "Arial Bold", 10);
b->setBackground(Chart::Transparent);
b->setLineStyleKey();
// Set the x and y axis stems to transparent and the label font to 10pt Arial
c->xAxis()->setColors(Chart::Transparent);
c->yAxis()->setColors(Chart::Transparent);
c->xAxis()->setLabelStyle("Arial", 10);
c->yAxis()->setLabelStyle("Arial", 10);
// Set the y-axis tick length to 0 to disable the tick and put the labels closer to the axis.
c->yAxis()->setTickLength(0);
// Add axis title using 12pt Arial Bold Italic font
c->yAxis()->setTitle("Ionic Temperature (C)", "Arial Bold", 12);
//================================================================================
// Add data to chart
//================================================================================
//
// In this example, we represent the data by lines. You may modify the code below to use other
// representations (areas, scatter plot, etc).
//
// Add a line layer for the lines, using a line width of 2 pixels
LineLayer *layer = c->addLineLayer();
layer->setLineWidth(2);
layer->setFastLineMode();
// Now we add the 3 data series to a line layer, using the color red (ff0000), green (00cc00)
// and blue (0000ff)
layer->setXData(viewPortTimeStamps);
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesA, 0xff0000, "Alpha");
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesB, 0x00cc00, "Beta");
layer->addDataSet(viewPortDataSeriesC, 0x0000ff, "Gamma");
//================================================================================
// Configure axis scale and labelling
//================================================================================
// Set the x-axis as a date/time axis with the scale according to the view port x range.
if (m_currentIndex > 0)
c->xAxis()->setDateScale(viewPortStartDate, viewPortEndDate);
// For the automatic axis labels, set the minimum spacing to 75/30 pixels for the x/y axis.
c->xAxis()->setTickDensity(75);
c->yAxis()->setTickDensity(30);
//
// In this demo, the time range can be from many hours to a few seconds. We can need to define
// the date/time format the various cases.
//
// If all ticks are hour algined, we use "hh:nn<*br*>mmm dd" in bold font as the first label of
// the Day, and "hh:nn" for other labels.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("align", 3600);
c->xAxis()->setMultiFormat(Chart::StartOfDayFilter(), "<*font=bold*>{value|hh:nn<*br*>mmm dd}",
Chart::AllPassFilter(), "{value|hh:nn}");
// If all ticks are minute algined, then we use "hh:nn" as the label format.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("align", 60);
c->xAxis()->setLabelFormat("{value|hh:nn}");
// If all other cases, we use "hh:nn:ss" as the label format.
c->xAxis()->setFormatCondition("else");
c->xAxis()->setLabelFormat("{value|hh:nn:ss}");
// We make sure the tick increment must be at least 1 second.
c->xAxis()->setMinTickInc(1);
//================================================================================
// Output the chart
//================================================================================
// We need to update the track line too. If the mouse is moving on the chart (eg. if
// the user drags the mouse on the chart to scroll it), the track line will be updated
// in the MouseMovePlotArea event. Otherwise, we need to update the track line here.
if (!viewer->isInMouseMoveEvent())
{
trackLineLabel(c, (0 == viewer->getChart()) ? c->getPlotArea()->getRightX() :
viewer->getPlotAreaMouseX());
}
// Set the chart image to the QChartViewer
delete viewer->getChart();
viewer->setChart(m_currentChart = c);
}
//
// Draw track cursor when mouse is moving over plotarea
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::drawTrackCursor(QmlChartViewer *viewer, int mouseX)
{
trackLineLabel((XYChart *)viewer->getChart(), mouseX);
viewer->updateDisplay();
}
//
// Draw the track line with legend
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::trackLineLabel(XYChart *c, int mouseX)
{
// Clear the current dynamic layer and get the DrawArea object to draw on it.
DrawArea *d = c->initDynamicLayer();
// The plot area object
PlotArea *plotArea = c->getPlotArea();
// Get the data x-value that is nearest to the mouse, and find its pixel coordinate.
double xValue = c->getNearestXValue(mouseX);
int xCoor = c->getXCoor(xValue);
if (xCoor < plotArea->getLeftX())
return;
// Draw a vertical track line at the x-position
d->vline(plotArea->getTopY(), plotArea->getBottomY(), xCoor, 0x888888);
// Draw a label on the x-axis to show the track line position.
std::ostringstream xlabel;
xlabel << "<*font,bgColor=000000*> " << c->xAxis()->getFormattedLabel(xValue, "hh:nn:ss.ff")
<< " <*/font*>";
TTFText *t = d->text(xlabel.str().c_str(), "Arial Bold", 10);
// Restrict the x-pixel position of the label to make sure it stays inside the chart image.
int xLabelPos = (std::max)(0, (std::min)(xCoor - t->getWidth() / 2, c->getWidth() - t->getWidth()));
t->draw(xLabelPos, plotArea->getBottomY() + 6, 0xffffff);
t->destroy();
// Iterate through all layers to draw the data labels
for (int i = 0; i < c->getLayerCount(); ++i) {
Layer *layer = c->getLayerByZ(i);
// The data array index of the x-value
int xIndex = layer->getXIndexOf(xValue);
// Iterate through all the data sets in the layer
for (int j = 0; j < layer->getDataSetCount(); ++j)
{
DataSet *dataSet = layer->getDataSetByZ(j);
const char *dataSetName = dataSet->getDataName();
// Get the color, name and position of the data label
int color = dataSet->getDataColor();
int yCoor = c->getYCoor(dataSet->getPosition(xIndex), dataSet->getUseYAxis());
// Draw a track dot with a label next to it for visible data points in the plot area
if ((yCoor >= plotArea->getTopY()) && (yCoor <= plotArea->getBottomY()) && (color !=
Chart::Transparent) && dataSetName && *dataSetName)
{
d->circle(xCoor, yCoor, 4, 4, color, color);
std::ostringstream label;
label << "<*font,bgColor=" << std::hex << color << "*> "
<< c->formatValue(dataSet->getValue(xIndex), "{value|P4}") << " <*font*>";
t = d->text(label.str().c_str(), "Arial Bold", 10);
// Draw the label on the right side of the dot if the mouse is on the left side the
// chart, and vice versa. This ensures the label will not go outside the chart image.
if (xCoor <= (plotArea->getLeftX() + plotArea->getRightX()) / 2)
t->draw(xCoor + 6, yCoor, 0xffffff, Chart::Left);
else
t->draw(xCoor - 6, yCoor, 0xffffff, Chart::Right);
t->destroy();
}
}
}
}
//
// User clicks on the Save Chart pushbutton
//
void RealTimeZoomScroll::saveChartImage(QmlChartViewer *viewer, QUrl url)
{
QString path = url.toLocalFile();
if (!path.isEmpty())
{
// Save the chart
BaseChart *c = viewer->getChart();
if (0 != c)
c->makeChart(path.toUtf8().constData());
}
}
© 2023 Advanced Software Engineering Limited. All rights reserved.